
Digital skills are the ability to take advantage of digital technology and communication.
Today, the digital world plays a huge role in our lives and the economies of every country. No business or worker is unaffected by changing technology. Its 2020 World Economic Forum report, presents the results of a survey of large companies around the world.
40% of workers need to improve their work skills to keep up with the digital age. In addition, 94% of executives expect their employees to learn new skills. And advances in technology could lead to a decline in the number of jobs in the future. 43% of companies surveyed are moving forward to reduce the number of workers.
Therefore, adapting and making full use of technology is an important factor in helping to develop the economy and skilled labor. When considering the case of Thailand, it was found that although Thais have access to the Internet quite a lot (80 percent of the total population).
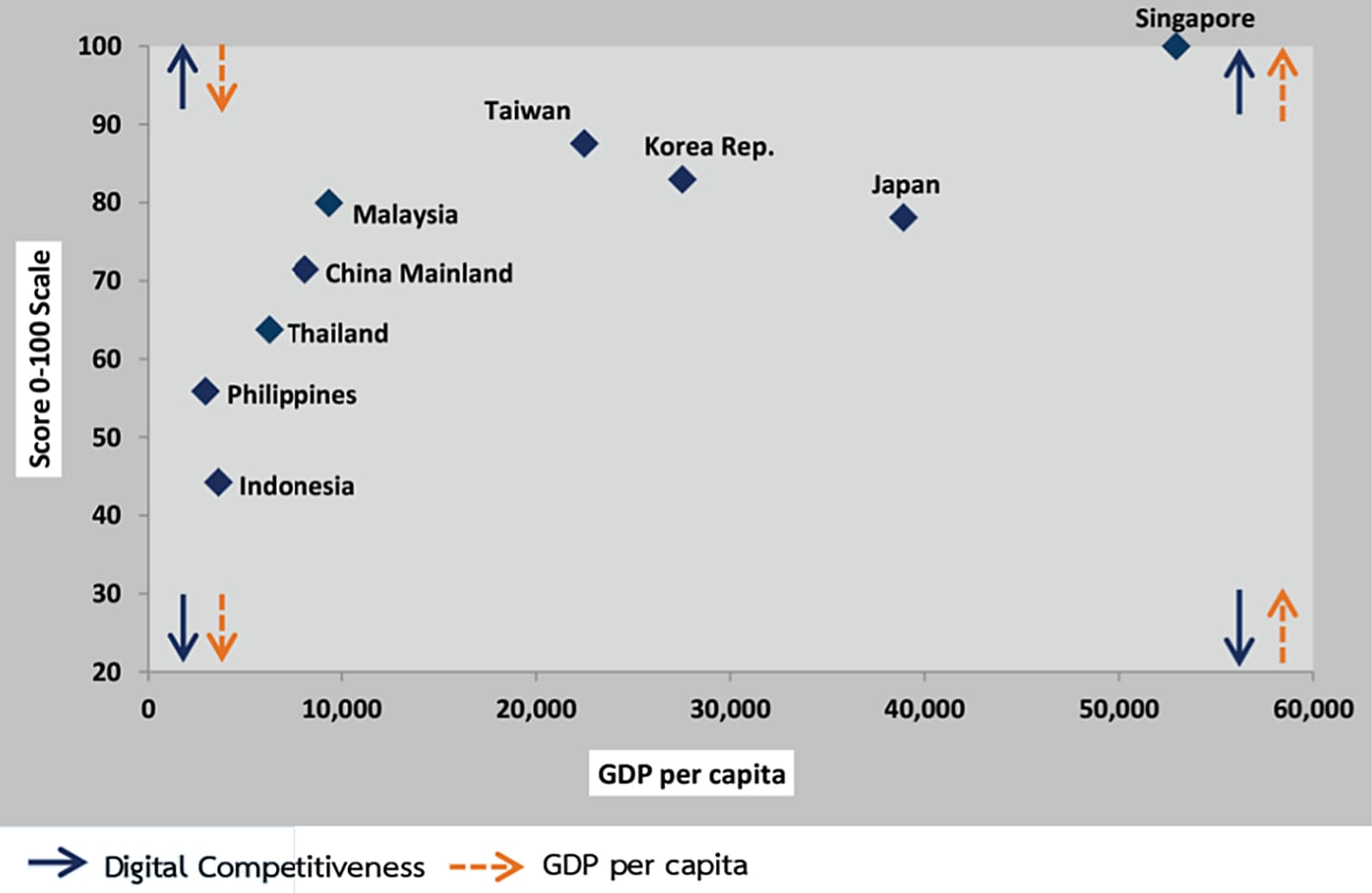
But according to the World Digital Competitiveness Ranking 2021 by the International Institute for Management Development (IMD), it is found that Thai people are not very digitally ready compared to other countries. Thailand ranks 38th out of 63 countries worldwide.
The IMD assessment is an overview. This article aims to study and measure the digital skills level of Thai workers in depth to help explore the readiness of Thailand’s digital skills to develop their digital transformation abilities.
Each country's digital competitiveness and GDP per capita.
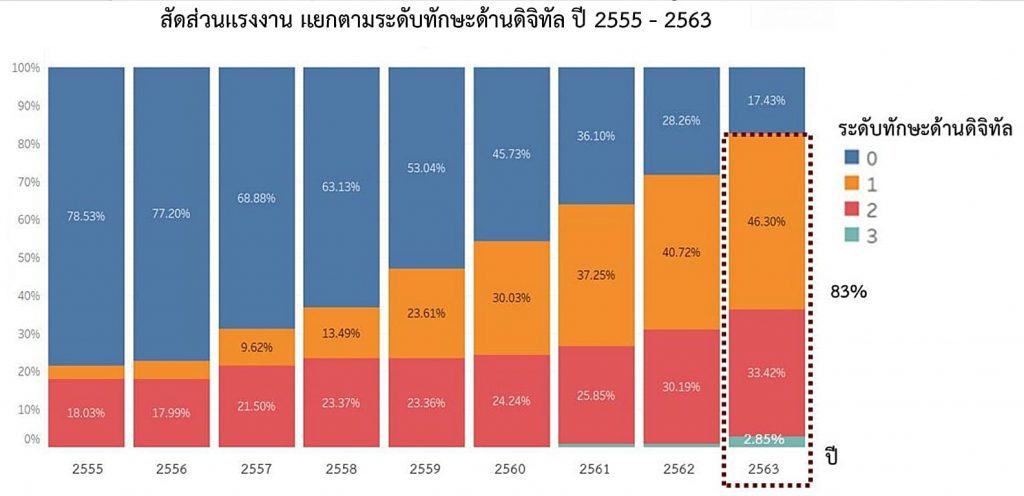
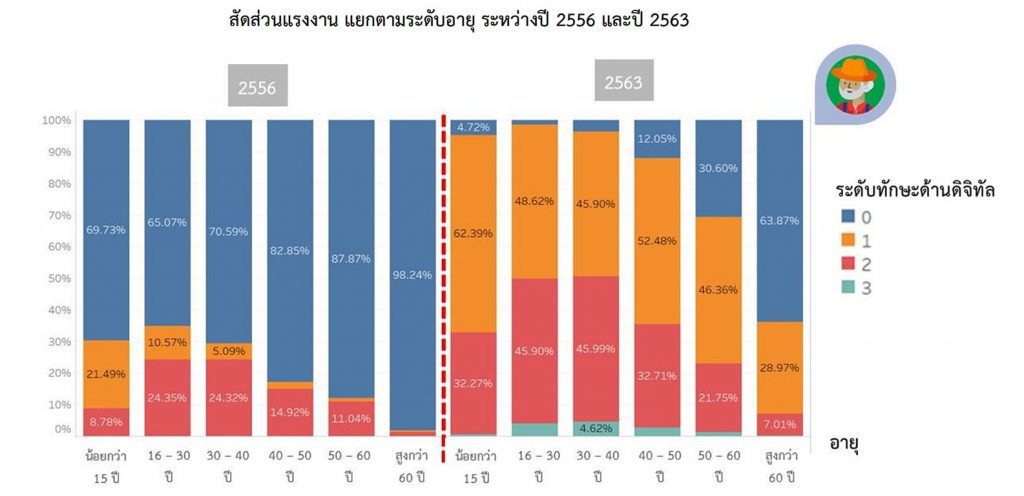
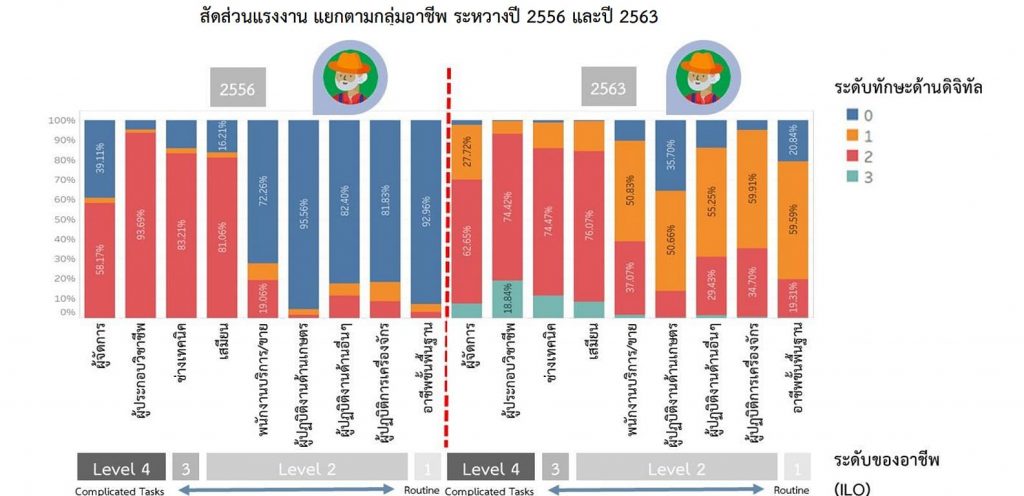
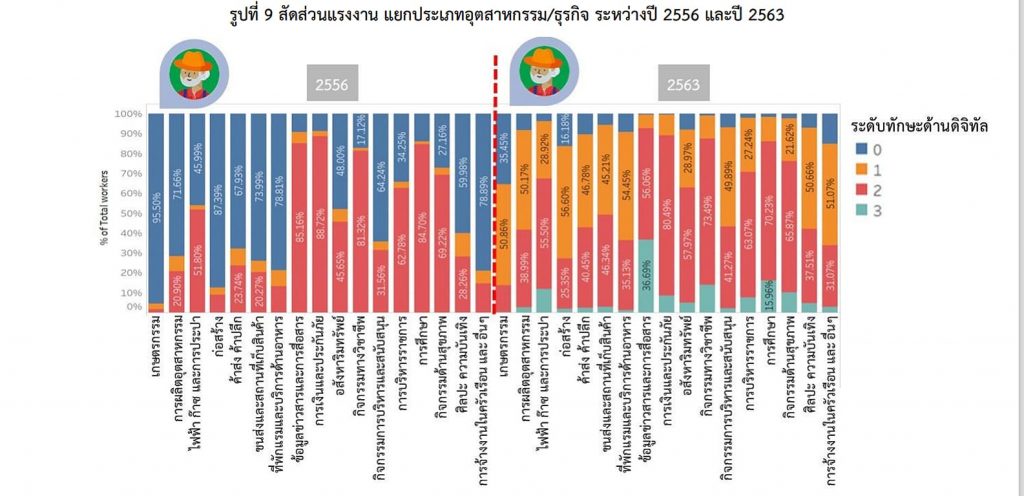
Conclusions from the survey on the use of information and communication technology in households (National Statistical Office)
It was found that in the past, Thai workers have adapted well to digital, as reflected in the proportion of workers who can use digital for their daily lives, which has greatly increased over the past 10 years, partly because Thai people have more access to the internet and lower mobile phone prices.
However, the availability of the workforce may not increase as it should, and much more needs to be done to keep up with future technological advances. This is reflected by the small proportion of the workforce using digital skills for work, growing slowly and concentrated. including the results of the digital competitiveness ranking. Particularly in terms of Thailand’s training and education, which has been steadily declining since 2018, although the demand for digitally skilled workers continues to increase. But the availability of a workforce that hasn’t changed to keep pace with demand could make the digital skill mismatch more serious in the future.
What’s your opinion? What can help Thai people develop digital skills for global competitiveness? Let’s share.
Reference : ธนาคารแห่งประเทศไทย